
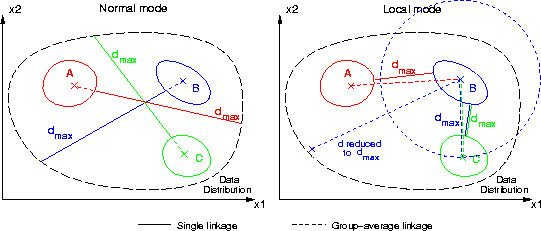
This command can be used to calculate a new data frame containing distances from all data records of a frame to several groups identified by a classified data. The distance can be measured as a) single linkage or b) group-average linkage (see figure below). Single linkage method locates the closest group member, and group-average first evaluates the average point for each group and calculates the distances between these group-averages and all data records. The result is a new data frame containing fields having the names of the groups identified in the classified data.
The calculation complexity of group-average linkage can be much smaller, but it cannot be used with certain types of data distributions. Part c) of the following figure depicts a problematic data distribution for group-average linkage.

There is also a local distance model available, in which all distances are limited to located minimum group-to-group distances. These minimum group distances are evaluated using single or group-average linkage according to chosen method.
| cldist | Calculate euclidean distances between data records and groups |
| -d <datain> | name of the original data to be used for distance calculation |
| -c <cldata> | classified data containing groupings |
| -dout <dataout> | distances from each vector to groups |
| [-dmax <maxfld>] | field name to use to store located maximum distance |
| [-gavg] | use group-average linkage instead of single linkage |
| [-local] | use locally limited distances |
This command creates new fields to a data frame containing distances from data vectors to groups of datavectors within the same data set. The groupings are identified by a classified data structure. The fields in output data are named according to group names. Located maximum distance can be stored for later use.
Example: For an example, see grpms (section 4.9).