
Figure 1: Data Analysis framework.
Some gallup data files might be easily analyzed. But, if there are more than 20 questions or statements and in some of them large values imply a positive attitude and in some others negative, it can be difficult to find proper interpretations to even a single person's opinions without proper analysis methods. Grouping of the people by analyzing their opinions is usually even more difficult.

Figure 1: Data Analysis framework.
Traditional mathematical methods usually require some kind of precedent hypothesis, which can be tested with mathematical accuracy. But in situations with thousands of answer forms containing 50 or more information fields, the calculation of variable to variable correlations or something similar can easily become a huge task. Also, what if no precedent hypothesis exists and we would just want to find groups of similarly thinking individuals?
The Self-Organizing Map (SOM) [1, 2] and its variants can handle this kind of situations. They let the people performing the analyses make their conclusions afterwards. The use of these neural network methods has in some cases also revealed deficiences in the original questions or statements presented to the people answering. This kind of post-analysis information can be very helpful in the task of constructing new questionnaires.
This paper also presents a single case study of performing neural network analyses on multidimensional data. The data used in this study has been gathered by presenting multiple choice questions to pupils of comprehensive schools in different parts of Finland. The data used in this study belongs to the Institute for Educational Research at University of Jyväskylä.
This study is part of the LAMDA 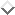 project. The analyses were performed using the Neural Data Analysis environment, NDA
project. The analyses were performed using the Neural Data Analysis environment, NDA  .
.